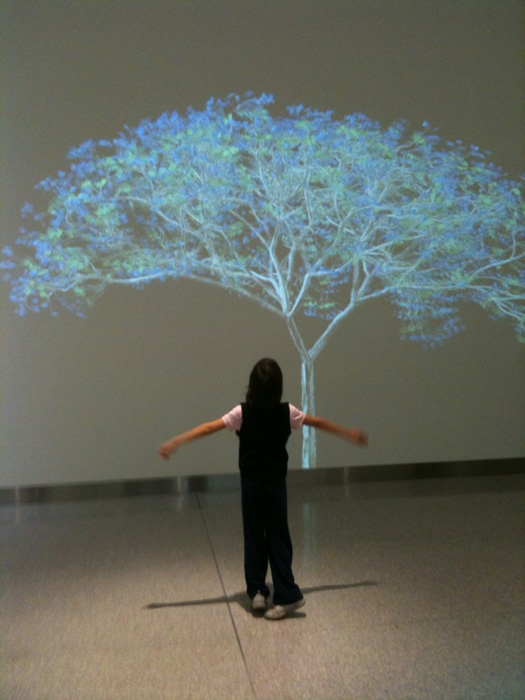
“While the patients apparently weren’t aware of the artwork as an important element of their bodily praxis in the environment when asked, their movements however indicated signs of their tacit awareness of the artwork’s presence, presumably as something infusing more ease and safety than having their back up against a white wall or looking at the art. As anthropologist Daniel Miller writes: “The surprising conclusion is that objects are important, not because they are evident and physically constrain or enable, but quite the opposite. It is often precisely because we do not see them” (Miller, 2010, p. 50).”